Energy efficiency and sustainability are paramount in today’s industrial environment. At the forefront of achieving these goals is a remarkable technology: the Industrial Heat Pump. A heat pump is a system capable of reversing the refrigeration cycle, thus providing both heating and cooling functions. Unlike traditional heating systems that often rely on burning fossil fuels, heat pumps extract heat from one area and transfer it to another using electricity, making them more environmentally friendly and cost-effective in jurisdictions with low GHG electricity systems that provide inexpensive power relative to the cost of natural gas.
A heat pump's functionality is centered around five key components: the evaporator, compressor, condenser, expansion valve and reversing valve, all working in concert with a special refrigerant essential for transferring heat.
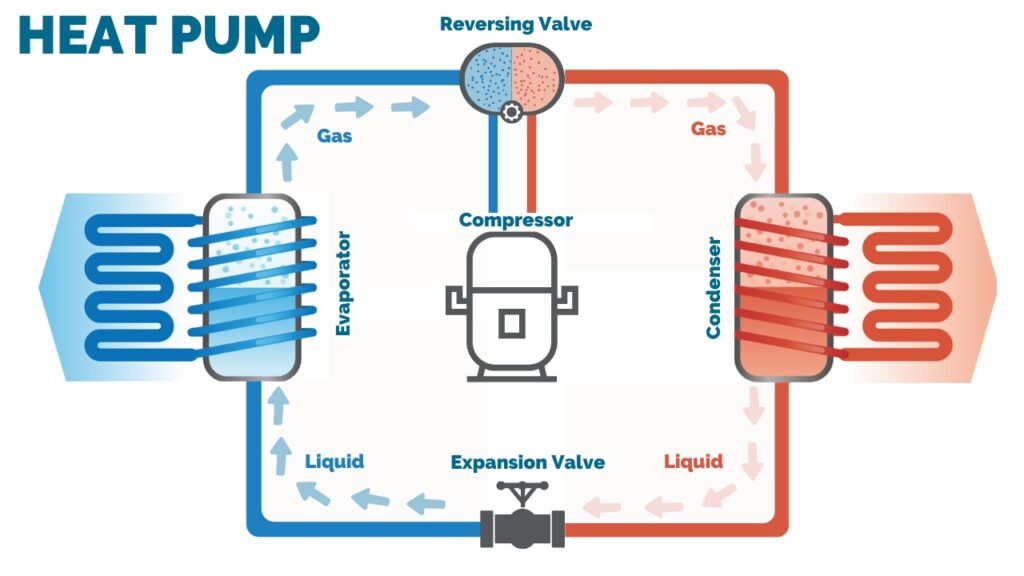
The operation of a heat pump is a continuous cycle. After passing through the expansion valve, the refrigerant returns to the evaporator, continuing the cycle to perpetuate the heating process. This ongoing cycle ensures a consistent transfer of heat, maintaining operational efficiency. By transforming latent heat sources into practical energy, heat pumps can offer significant energy cost savings and contribute to reducing carbon emissions, thereby aligning with global sustainability goals.

At the core of a heat pump system lies its refrigerant—a fluid circulating through the system, alternately evaporating and condensing to absorb and release heat. With the reversing valve directing the flow of refrigerant, the heat pump provides both heating and cooling functions, offering versatility and convenience for typical HVAC applications. During the heating mode, the outdoor coil functions as the evaporator, absorbing heat from a low-temperature source like outdoor air, water, or the ground. This heat is then compressed by a compressor to increase its temperature and pressure before circulating it through an indoor coil, which acts as the condenser, releasing warmth into the indoor space. Conversely, in cooling mode, the roles are reversed: the outdoor coil serves as the condenser, expelling heat outside, while the indoor coil acts as the evaporator. The heat pump extracts heat from indoors, effectively cooling the indoor environment by expelling it outside.
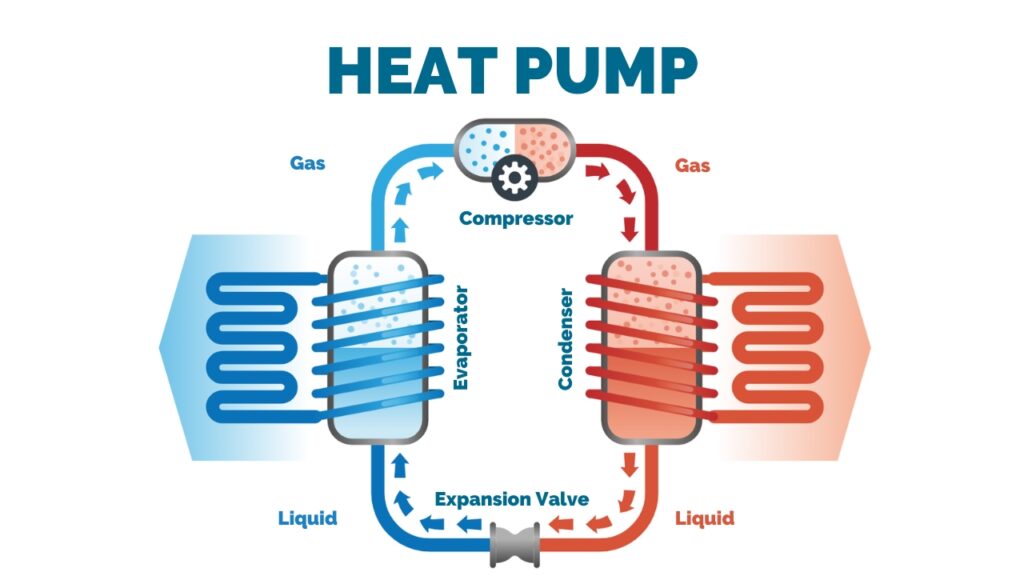
In industrial settings, heat pumps serve as indispensable tools for optimizing processes and achieving both economic and environmental objectives. Unlike traditional heating methods reliant on combustion, industrial heat pumps are engineered to operate in the reverse refrigeration cycle, efficiently providing heat to processes by using electricity instead of gas. This design enables companies to capitalize on the economic benefits of utilizing relatively low-cost hydroelectric power to provide heat. Industrial Heat pumps boast lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel-based heating systems, particularly in jurisdictions where the electricity infrastructure has a low GHG footprint, aligning with corporate sustainability goals and regulatory requirements. Consequently, the widespread adoption of heat pumps in industrial operations underscores their pivotal role in balancing economic competitiveness with environmental responsibility.
As the focus on sustainable and energy-efficient solutions grows, the future of industrial heat pumps looks promising. Technological advancements are enhancing their effectiveness and broadening their applications. Innovations like variable speed compressors, advanced heat exchanger designs, and integration with smart control systems are making heat pumps more effective and adaptable to a wider range of industrial applications.
Industrial heat pumps are an important part of the movement towards more sustainable industrial processes. By utilizing latent environmental or waste energy sources, they convert these into practical heat. This not only offers considerable energy savings but also supports global ecological sustainability objectives by reducing carbon emissions. Understanding these systems and their varieties empowers industries to make informed decisions about their heating solutions, aligning economic and environmental objectives.
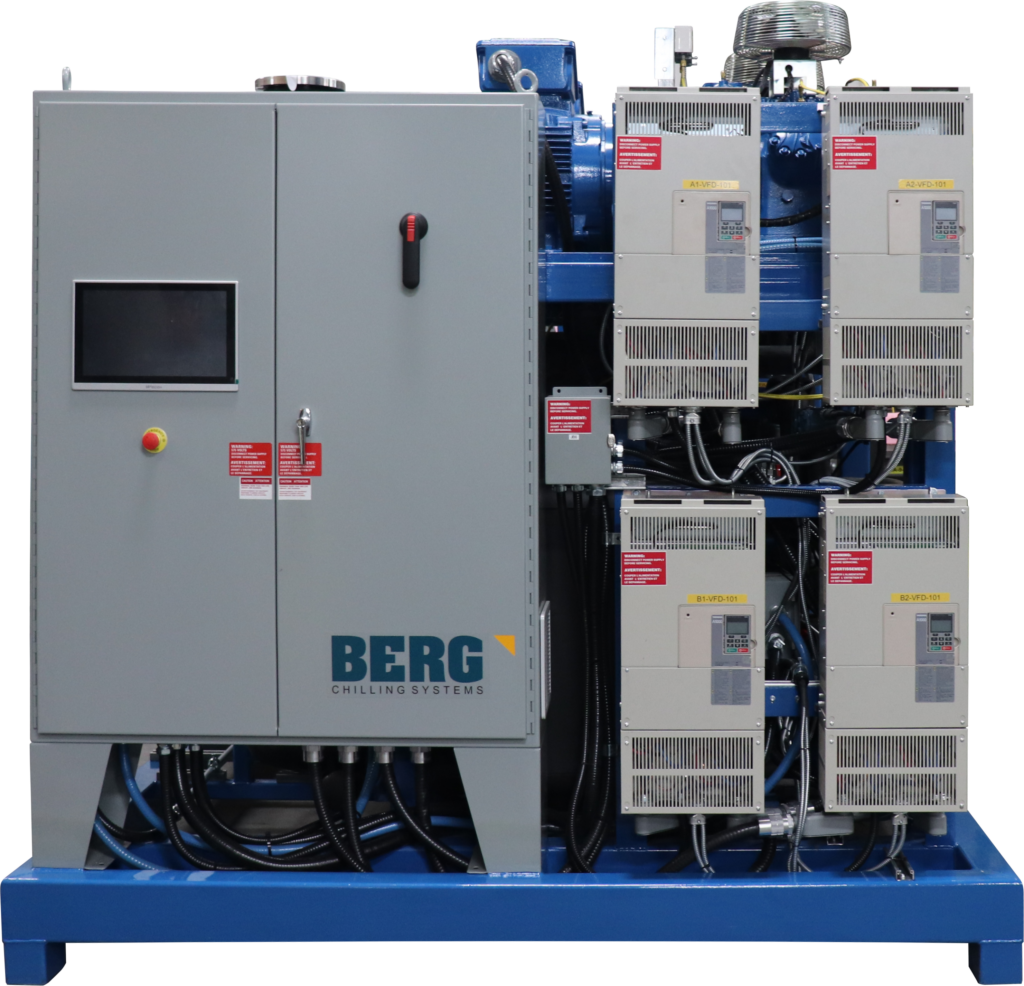
At Berg, we understand the crucial role heat pumps play in today's industrial landscape. With over 50 years of experience, we have partnered with various sectors to provide custom-engineered industrial heat pumping systems. Our commitment to innovation and quality ensures that our heat pumps are not only tailored to your specific needs but also comply with the highest industry safety standards. Whether it’s for waste heat recovery or industrial process cooling, our systems are engineered to adapt to diverse applications. They are capable of producing hot air, water, steam, and direct material heat, meeting the varied demands of industries.
Choosing Berg means partnering with a leader in industrial heat pump technology. Our experience, combined with our commitment to custom solutions and comprehensive service, makes us the ideal choice for your industrial heating and cooling needs. We're not just providers; we're partners in your journey towards more efficient, sustainable industrial operations.
Contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you achieve operational excellence with our state-of-the-art heat pumping systems.